So, you’ve got bed bugs. It’s OK. Bed bugs have been part of human society from the beginning.
They have been found in Egyptian tombs and were mentioned in texts dating back to the time of Aristotle. However, in the fight against bed bugs, you have something that Aristotle didn’t have… the internet!
Today, you can learn about bed bugs and the most effective treatment methods from experts in the pest management industry.
Let’s dive right in…
Bed bugs have enjoyed a resurgence in recent years. Bed bugs were nearly eradicated in the United States due to the widespread use of pesticides such as DDT.
Besides, general pest management practices have shifted to only using pesticides indoors only when necessary. In the past hotels would routinely treat guest rooms with pesticides, and this would prevent a bed bug infestation.
Bed bugs have also become resistant to many of the pesticides they encounter in their travels. However, using scientific advancements and a biological understanding of bed bugs, it is possible to get rid of bed bugs and sleep peacefully again.
In this guide, we will explore the best methods for getting rid of bed bugs. We will discuss why they are notoriously hard to get rid of and how long you should expect the extermination process to take.
Now:
There are many different treatment methods utilized to kill bed bugs and you can weigh the benefits and negatives of each method.
We all want a healthy home for our family; with a little boost of knowledge, you can feel confident in the bed bug elimination method that you choose. Whether you are trying to get rid of bed bugs from a single-family residence, an apartment, or even a hotel or nursing home, with the treatment options available today, it is possible to get rid of bed bugs.
How to Check for Bed Bugs
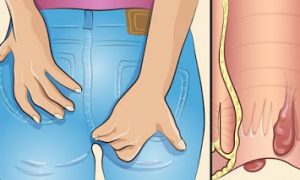
Do you wake up to mysterious bites on your shoulder or legs? Do you suddenly see reddish-brown spots on your sheets? If you suspect that bed bugs may be the cause, a thorough inspection and prompt treatment can be the difference between an introduction and a full-blown infestation. Finding and treating a minor bed bug infestation is less costly and simpler than dealing with a bed bug in every nook and cranny of your bedroom. However, a minor bed bug infestation can be hard to find. You need to know how to check for bedbugs.
Bed bugs are small, flat, oval-shaped insects. Adults are about the size and shape of an apple seed. Although they are not known to spread diseases, they crawl from their daytime hiding places to feed on resting humans. Bed bugs are small, but visible to the naked eye; an adult bed bug measures between 6 to 9.5mm. Bed bugs are usually brown in color, but after a fresh feeding, their body becomes swollen and red. Like other insects, they have 6 legs and 2 antennae.
Bed Bug Behavior
Bed bugs are excellent hitchhikers. They are often brought into your home in a purse, a bag, a backpack, or a suitcase. Bed bugs are most commonly found on and around the bed, but they can be located anywhere that has human contact for prolonged periods of time. Bed bugs can crawl into your bag on an airplane or train, while at the movie theater, or during a ride with a friend or rideshare service. You then bring your bed bug contaminated bag into your bedroom, and voila, the bed bug nightmare has begun.
Although they cannot fly or jump, bed bugs are capable walkers and climbers. They can easily climb the metal or wooden legs of furniture to access a blood meal if there is even a slight texture to the finish. Bed bugs have been observed to walk 3-4 feet per minute! They hide in tight harborages during the day and happily travel between 5-20 feet from their hiding place to feed upon their host. They locate a potential host by homing in on the carbon dioxide exhaled when we breath and the heat that emanates from our bodies. Once they locate a potential host, bed bugs pierce the skin and feed for between 3-12 minutes.
Most people do not wake up when bed bugs are in the act of feeding, and every person responds differently to a bite.
What to Look for when Checking for Bed Bugs
Bed bugs are so small and flat that they can hide anywhere that a credit card can fit. They are generally found close to the bed, where their food source is located, but as an infestation grows the prime hiding places become overcrowded and they expand their reach. When checking a room for bed bugs, carefully inspect cracks and crevices on or near the bed. Have a strong flashlight, a flat-edged object like a paint scraper or credit card, and perhaps a magnifying glass as well. To adequately check for bed bugs you may have to take apart the headboard or the bed frame.
When checking for bed bugs, look for every life stage. By locating and acknowledging the presence of eggs, immature bed bugs, and adults, you can gauge the severity of the infestation.
- Live adult bed bugs – visible to the naked eye, about the size of an apple seed
- Bed bug nymphs (immature) – smaller than the adult (between 1.5mm – 4.5mm), translucent to tan in color, especially if unfed
- Bed bug eggs – Very difficult to see with the naked eye, about the size of a pin head (1mm) and pearly-white in color
- Molted Skin – As nymphs progress to adulthood, they shed their skin 5 times. This skin is left behind in harborages and crevices.
- Feces – small dark spots which may bleed and smear into the fabric
Where to Check for Bed Bugs
Some common bed bug hiding places include:
- Seams and tufts of the mattress and box spring
- Near the piping or tag on the mattress and box spring
- Cracks and crevices of the headboard, footboard, and bed frame
- Joints (crevices) of drawers and other bedside furniture
- Seams of couches or chairs in the room
- Behind electrical outlets on the wall
- Inspect wall hangings and picture frames
- Inspect the folds of curtains
- Inside of electrical appliances such as an alarm clock or docking station
- Inspect where the carpet meets the wall
- Check behind baseboards and other trim pieces
While checking your home for bed bugs it is important to determine the breadth of the infestation. Continue to check areas further away from the source of the infestation until you find no evidence of bed bugs. As you check your home for bed bugs, be sure not to cross-contaminate rooms and actually introduce bedbugs where they did not exist before. As you check your home for bed bugs, make notes of where and what you find. Save samples too. Larger specimens can be scooped up and placed in a ziplock bag. For smaller eggs and nymphs a piece of packing tape is great to “stick” it to the insects. Then place the tape in a ziplock bag to secure.
Now that you know how to check for bed bugs, test your skills the next time you check into a hotel room. Do this before you unpack any clothing and situate in the room. Lift the sheets and perform a cursory check of the mattress and bed frame. If you find any evidence of bed bugs, capture them and report the incident to management immediately.
If you think you may have bed bugs, call Nextgen Pest Solutions. Our professionals can thoroughly inspect your home for bed bugs and our treatments give you the peace of mind to rest easy again.
Are Bed Bugs Hard To Get Rid Of?
The short answer is yes. This is not a problem that can be solved by reaching for the can of roach spray you keep under the kitchen sink.
Even professional pest control companies generally expect at least two treatments to completely get rid of the bed bugs from your home. Why are bed bugs so hard to get rid of? There are several reasons that bed bugs are notoriously hard to eliminate.
Here’s the deal:
- Pyrethroid (Pesticide) Resistant – Pyrethroids are a class of chemicals that are commonly used in pest management applications. Most pyrethroids have low toxicity to mammals (people and pets) and birds, are fast-acting, and require low doses of active ingredients to kill insects. However, some bed bugs have developed resistance to this class of chemicals. Entomologists have compared the death rates of bed bugs reared in the laboratory for 30 years (no exposure to pyrethroids) vs bed bugs collected from homes around the country. The lab-reared bed bugs had a 100% death rate when a pyrethroid insecticide was introduced. The field-collected bed bugs showed near immunity from the pyrethroid pesticides. There are varying degrees of resistance depending on the bed bug population, but all the experts agree that pyrethroid resistance contributes to the difficulty in getting rid of bed bugs.
- Bed Bugs Multiply Quickly – Another factor making it hard to get rid of bed bugs is how quickly they multiply. The number of eggs a female bed bug will lay in her life depends upon her access to blood meals. The average lifespan of a bed bug is about one year. Bed bugs usually feed every 3-7 days if a meal is available. One female can lay about 113 eggs in her lifetime. Under optimal conditions, a present host, and comfortable air-conditioned temperature, bed bug populations can double every 16 days.Video Player00:0000:07
- Bed Bug Behavior – The activity, habits, and behavior intrinsic to bed bugs make them hard to get rid of. Bed bugs have a secretive lifestyle; they are active at night and congregate together in small cracks and crevices during the day. Their flat bodies enable them to fit into a crevice no wider than a toothpick. They prefer to stay close to their next meal (your bed or sofa) and often gather in the tufts and folds of mattresses, box springs, bed frames, headboards, and side tables. They are also often found behind wall plates and baseboards. Bed bugs do not have a central “nest” like ants or termites. They are prone to wandering. If a single pregnant female remains after a bed bug treatment the infestation process can begin again. Bed bug behavior coupled with their life cycle makes them a very hard pest to get rid of.
The current bed bug outbreak in the United States began in the 1990s. It is not yet ingrained in our culture to be vigilant when staying at hotels or vacation rentals, or thoroughly inspecting used furniture that you bring home.
One night’s stay in an infested room is enough to bring bed bugs home with you in your bags. Once introduced, it often takes several months to realize the itchy welts on your skin are from bed bugs.
They hide during the day, and the bite itself is painless. An introduction quickly becomes an infestation. Resistance to chemical treatments, their cryptic lifestyle, and rapid rate of reproduction combine to create a situation where bed bugs are hard to get rid of.
Stay with me here while we see how quickly we can get rid of bed bugs:
How Long Does It Take to Get Rid of Bed Bugs?
Getting rid of bed bugs is a process, no way around that. How long it takes to get rid of bed bugs depends upon which elimination method you choose, the severity of the infestation, and the thoroughness of the treatment.
A bed bug treatment using heat kills bed bugs immediately, but there is no residual. A chemical bed bug treatment can take a few weeks, but it leaves a residual which provides continued protection from bed bug re-infestation.
The size and severity of the initial infestation is also a factor in determining how long it will take to get rid of bed bugs. From the time you realize you have bed bugs to sleeping worry-free, do not be surprised if it takes at least 4-6 weeks.
Regardless of the treatment method, you select, finding the right licensed and insured pest control company to partner with can take time. Interview multiple professionals and ask detailed questions regarding their experience, procedures they use, and their success rates.
Before you commit or sign any contract, find out when they are available to do the initial treatment and ask about their practice for follow-up appointments if they are needed.
Another factor that affects how long it takes to get rid of bed bugs is understanding that you will be responsible for preparing the room for treatment.
Bed bugs hide in the smallest of crevices including the joints on your bedside table. Your pest control company will give you a prep sheet of things you need to do before they can treat the room.
Allow yourself plenty of time to accomplish this before they come to treat you. Not only does proper preparation increase the effectiveness of the treatment, but insufficient preparation may also cause the company to reschedule/delay the treatment.
- Traditional Insecticide Treatment – If you choose a traditional insecticide bed bug treatment, how long it takes to get rid of the bed bugs can vary. Bed bug eggs hatch between 6 and 9 days after they are laid. For this reason, multiple treatments are often necessary which extends the timetable for fully getting rid of bed bugs. Also, be realistic with the scope and severity of the problem. If you are concerned about killing bed bugs fast, do not under-represent the locations where you have seen bed bugs to your Pest Management Professional. If you have seen them in both the living room and the bedroom, treat both of these rooms at the same time. This prevents reinfestation and allows you to quickly get rid of the bed bugs.
- Heat Treatment – Heat treatments are the quickest way to kill bedbugs. This is not a turn up the heater and goes out to lunch solution, but it can be accomplished in one appointment from the pest control company. Licensed professionals with specialized equipment will heat your room to between 135°F (57.2°C) and 145°F (62.7 °C). Thermometers are placed around the room and watched closely to ensure the air is heated enough to kill bed bugs but not hot enough to cause damage. Bed bugs and bed bug eggs die immediately at 122°F (50°C). This treatment generally takes between 6 to 8 hours and requires careful monitoring by the technician and preparation from you the homeowner. If waiting 2-3 weeks to get rid of bed bugs is not an option for you, successful heat treatment can get rid of bed bugs in as little as an afternoon.
- Do-It-Yourself (DIY) – If you are inclined to treat bedbugs yourself, you can buy almost everything the professionals use, but it will inevitably take longer to get rid of the problem. There are excellent guide videos online to show you how to inspect and treat, but this treatment method may take longer to fully eliminate bed bugs from your home. You must take the time to discern between various products to learn how to safely and properly apply them. Pest management professionals often have years of field experience and high-level training. They have personally observed bed bug behavior for years and successfully gotten rid of bed bug infestations. If you are tackling this job yourself, regular and thorough inspections and prompt re-treatments are necessary to successfully get rid of bed bugs. Remember, if you miss one spot during your bed bug treatment, you may have to start the battle over from the beginning. A DIY approach to bed bug elimination is not fast or easy, but it certainly can be done.
How to Get Rid of Bed Bugs Fast
Once you have determined you have bed bugs creeping into your bed at night, you need to act fast. The longer you allow the infestation to proceed untreated the more expensive and time-consuming it becomes to get rid of the bed bugs. But don’t panic and throw out your mattress thinking your problem is solved; it is not.
Here’s the deal:
Educate yourself on the various treatment options and determine which method aligns with your priorities and budget. Generally speaking, getting rid of bed bugs completely is not a fast, easy, or inexpensive process.
- DIY First Steps to Control – If you need to make some bed bug killing progress fast while waiting for your treatment appointment try these remedial measures. Clear all clutter, put it in a plastic bag, and dispose of it outside. Vacuuming alone will not solve a bed bug infestation, but it can help keep their numbers down. Be sure not to move items from room to room as that will spread your problem to other areas of the house. Clutter and trash should be sealed in a bag and immediately taken outside. After vacuuming bed bug-infested areas, immediately clean the vacuum outside. Scrub infested areas with a stiff brush to dislodge the eggs and vacuum with a powerful vacuum. Using the crevice attachment, vacuum along all bed seams, cracks, crevices, and baseboards. If you have a strong heat steamer, you can kill bed bugs quickly making slow passes on your bed and bed frame with steam. Stay away from the wall outlets with steam! Launder all the bedsheets and linens and dry on the hottest setting your dryer has. To quickly kill bedbugs toss shoes, stuffed animals/plush toys, blankets, pillows, seat cushions, and fabric bags in the dryer for at least 1 hour. Consider placing a mattress and box spring encasement on your bed and bed bug traps on the feet of your bed. Each of these actions will get rid of some bed bugs quickly, but will not solve the problem without other intervention.
- Heat Treatment – If your main concern is killing bed bugs fast, heat treatment may be a good option for you. Heat treatments can kill bed bugs in one day by a licensed pest control company. The affected room is heated to between 135°F (57.2°C) and 145°F (62.7 °C). Some experts believe the rising temperature in the room lures the bed bugs from the daytime hiding spots. When a bed bug (and bed bug eggs) reaches 122°F (50°C) they immediately die. A successful bed bug heat treatment requires a highly skilled technician. Mattress, furniture, drywall, and concrete are excellent insulators. If any bed bug refuge doesn’t quite make it to bed bug-killing temperature the treatment will fail. Likewise, too much heat can destroy electronics and sensitive items. The appointment for this service will take about 8 hours to complete. Although heat kills bed bugs quickly and efficiently, there is no residual effect. Unless a residual pesticide is applied in conjunction with the heat, any bed bug that may hitchhike from another part of the house can begin the infestation again.
- Traditional Chemical Bed Bug Treatment – An insecticide-based treatment is a much more affordable option than heat treatment, but it does require patience. Bed bugs that are accessed directly during your treatment will die quickly. However, most of the time bed bugs contact the insecticide indirectly, meaning they walk on it during their evening search for a meal. Bed bugs only come out of hiding for a meal every 3-7 days. Most insecticides do not kill the bed bug eggs either. A follow-up pesticide application may be necessary to kill the nymphs that have hatched from the eggs since the first application. The goal of this application is to kill the nymphs before they become adults that are capable of reproducing. Although chemical control for bed bugs is effective, it is not the fastest way to kill bedbugs.
Can You Get Rid of Bed Bugs on Your Own?
Yes, you can get rid of bed bugs on your own. With patience, perseverance, knowledge, and the right products, you can get rid of bed bugs without an exterminator. Do-it-yourself bed bug control can fit nicely into your budget and schedule, but it is a large undertaking.
Be warned though, that if you make mistakes during a DIY bed bug treatment you will find yourself in a cycle of continual treatment. This means you will spend quite a bit of money repurchasing pesticides and applying more pesticides to your bedroom and mattress than if you had called a professional.
There are many products very cleverly marketed for bed bugs that will not solve your problem. As all DIY homeowners know, success is found in the planning and learning phase. Know the products you are purchasing and how and if they interfere with one another.
Have realistic expectations, but with diligence and consistency, you can get rid of bed bugs yourself. Here are the steps we recommend if trying to get rid of bed bugs yourself.
- Identify – If you are treating bed bugs yourself, you have to verify that what you are seeing is indeed a bed bug. Bed bugs are small, but they can be seen with the naked eye. Once you catch a specimen many counties offer extension services that can positively identify the specimen. Treating your sleeping area with pesticides without confirmation of active bed bugs can lead to unnecessary pesticide exposure.
- Inspect – To successfully get rid of bed bugs yourself, you must know the locations and severity of the infestation. As a general rule, a recent infestation will be confined to areas in or around the bed. A severe infestation may have spread to other bedrooms or the living room. Use a bright flashlight and paint scraper or even a credit card to carefully inspect the tufts and seams of mattresses, turn the box spring and nightstand upside down, and carefully inspect all the cracks and crevices. Disassemble the headboard and bed frame checking carefully for live bedbugs, skins from molting nymphs, and blackish fecal spots. The edges of baseboards should always be closely examined as well. If an upholstered sofa or recliner is used for sleeping, check the folds of the fabric and underneath thoroughly. Once you have determined an active bed bug infestation and the severity and locations of the infestation, you need to order your chosen pesticides and prepare the room to get rid of bed bugs yourself.
- Treatment – A successful Do It Yourself bed bug treatment will use a combination of a few different products. You will choose a product for the mattress, a product for cracks and crevices other than the mattress, and pesticide-based dust for around electrical outlets and other inaccessible areas. When deciding which products to use, ALWAYS READ THE LABEL. The label is the law. The allowable placement and application of each product are described on the product label. Most insecticides are not allowed to be applied to mattresses, but a few are. Some products leave a residual while others do not. Some products are fast-acting while others are not. We recommend encasing your mattress and box spring with a bedbug-proof cover to prevent future infestations. The key to a successful do-it-yourself bed bug treatment is you must be thorough. Leave no crevice in the room untreated.
- Monitor – After you put your freshly laundered sheets back on your bed, you must still actively monitor and retreat. Bed bug eggs will hatch after about a week and they need to be killed so they do not become adults capable of reproducing. Place bed bug traps under the feet of your bed and furniture. Bed bug traps prevent bed bugs from crawling from the floor up into your bed or furniture, they also serve to monitor the infestation. Repeat the treatment every 7-10 days until there is no evidence of bed bugs in the home.
As Youtube has shown us, we can do anything, including getting rid of bed bugs ourselves. With thorough inspections and applications, and re-treatments as soon the need arises, expect 6-8 weeks to a bedbug-free home.
How To Get Rid of Bed Bugs Naturally
When treating a bed bug infestation, it is understandable to be concerned about the chemicals being sprayed on and near your bed. How to kill bed bugs naturally is a very common question with a somewhat complicated answer.
Bed bugs are hard to kill; if the answer was as simple as spritzing lemongrass oil around your bed, the professional bed bug industry would not exist. A study conducted in 2018 found that professional pest control companies performed over 1 million bed bug exterminations in the United States with gross revenue of over $600 million.
Bed bugs reproduce very quickly in the ideal environment of a temperature-controlled bedroom with a blood meal available nightly. A bed bug population can double every 16 days.
They are small, elusive, and hide during the day, making it impossible to physically remove or kill every individual bed bug. Natural products like essential oils and other home remedies cannot kill bed bugs as quickly as they reproduce.
Home Remedies for Bed Bugs
There are many natural ways to kill bed bugs, some work, others do not. Completely getting rid of bed bugs naturally will take a combination of products and treatments. If you don’t eliminate the bed bugs, the infestation will continue and become more difficult to control.
Before you attempt any natural home remedy for bed bugs remember that even “natural” and organic substances can cause skin irritations and reactions, especially if used in excessive quantities. We do not recommend using any products to kill bedbugs that are NOT approved by the EPA.
- Vacuum – An easy and accessible way to naturally kill and remove bed bugs is with your vacuum cleaner. This will not eliminate your bed bug problem but helps to greatly reduce their numbers. Vacuum cracks and crevices include tufts, seams, zippers, and the trim of beds and upholstered furniture where bed bugs can hide. Be sure to throw away the vacuum bag outdoors to avoid spreading bed bugs to other areas of the house.
- Steam – Bed bugs and their eggs die at 122°F (50°C). The high temperature of steam 212°F (100°C) immediately kills bed bugs. Apply steam slowly to the folds and tufts of mattresses, along with sofa seams, bed frames, and corners or edges where bed bugs may be hiding. Be careful though, steam may damage some finishes and keep steam away from electricity. Steaming every few days is a natural way to kill bed bugs, but may not provide 100% relief.
- Protect Your Bed – It is not necessary or advisable to throw out your mattress at the first sign of bed bugs; the bed bugs will infest your new bed. Instead, invest in a bedbug-proof mattress and box spring encasement. These completely encase your mattress and the zipper is so small that even the smallest of nymphs can not escape. Bed bugs can neither come out of your bed to bite you, nor get into your mattress and box spring. Installing these natural bed bug barriers greatly helps in your fight against bed bugs.
- Dryer Sheets – It is circulated online that rubbing dryer sheets on your bed and furniture will repel bed bugs. There is simply no data to support this. Bed bugs are drawn out from their hiding spots from the heat of our resting bodies and the CO2 we exhale. They will not choose to starve to avoid the scent of a dryer sheet.
- Essential Oils – There are many essential oil recipes online claiming to repel bed bugs. If you have an infestation, you need to do much more than attempt to repel them; you need to kill them. Entomologists at Rutgers University have conducted experiments with various oils. In a pristine laboratory setting where the oils were directly applied to bed bugs, many of the essential oils had very low mortality rates in bedbugs. The oils with the greatest promise are silicone oil and paraffin oil. Researchers theorize that silicone oil and paraffin oil suffocated the bedbugs, but much more research is needed before this can be an effective home remedy for bedbugs.
- Alcohol – Spraying alcohol on your mattress and furniture is not a natural remedy for bed bugs. Studies show that directly spraying a bed bug with rubbing alcohol will kill it only 50% of the time. Keep in mind the cryptic lifestyle of the bedbugs; they are congregating out of sight and out of reach when you are awake. They only become active at night. You can not get rid of bed bugs by only killing the ones you easily see walking across your bed. Besides, rubbing alcohol is a flammable material and could cause a fire hazard.
- Ultrasonic Pest Repellers – The Journal of Economic Entomology published a study that tested whether bed bugs were either repelled or attracted by these ultrasonic noise devices. The study found that these devices had no impact on the bed bugs; they were neither attracted to nor repelled from the noise.
Natural Pesticides for Getting Rid of Bed Bugs
- Silica Dust or Diatomaceous Earth – Diatomaceous Earth, or DE, is not a repellent but it is not a traditional pesticide. It is finely ground-up remains of fossils of small aquatic animals called diatoms. The skeletons of diatoms are made up of silica which has sharp edges. When bed bugs and other insects come into contact with the diatomaceous earth the sharp edges cause abrasions and cut the bed bug’s exoskeleton. Eventually, the bed bug dehydrates and dies. This natural dust can be spread around the perimeter of the room, in cracks and crevices, and on the mattress and box spring. It kills bedbugs slowly, but it remains effective so long as it is left undisturbed.
- Natural/Botanical Pesticides – Pesticide products must be registered with the EPA unless they are natural and generally regarded as safe. Natural or botanical pesticides receive a 25B registration from the EPA. There are many 25B products available marketed as natural bed bug treatments. They contain mixtures of plant oils and often have strong odors when applied. Because they are not tested by the EPA, the manufacturers are not required to show data that they work! Before buying any of these products you should look for independent laboratory testing to determine their efficacy. If you choose this route, please remember that even all-natural and organic products can cause skin irritations.
- Aprehend™ – Aprehend™ is a natural biopesticide that has proven highly effective against bed bugs. It is comprised of Beauveria bassiana fungal spores. Beauveria bassiana is a natural fungus that is harmless to humans but causes disease in insects. Researchers at Penn State University developed a delivery method for applying these spores to surfaces to treat bed bugs. The formulation is applied with a proprietary sprayer and the spores remain dormant on the surface until a bed bug walks through them. The fungal spores attach to the bed bug’s skin and germinate after about 20 hours. After the spores germinate, the fungus gains access to the bed bug’s bloodstream and within 3-7 days the bed bug dies from a fungal infection. Research on Aprehend™ also suggests that bed bugs transfer the disease-causing spores to other bed bugs that have not yet come into contact with Aprehend™. Bed bugs live together in tightly packed harborages which facilitates the spread of the fungal spore. A significant advantage of Aprehend™ is the long-lasting residual effect. An Apprehend™ barrier remains active for up to 3 months if it is left undisturbed. An Aprehend™ bed bug treatment is a natural bed bug remedy that should be considered. Something like Ortho Home Defense Max may also work.
Natural Bed Bug Control with No Pesticide
There are natural ways to get rid of bed bugs without chemicals, however for the most part it requires the assistance of a licensed pest control company. These methods utilize specialized equipment and are not considered home remedies for bed bugs.
- Cryonite Treatment – One way to kill bed bugs without using chemicals is by freezing them. A Cryonite machine converts liquid carbon dioxide into particles of dry ice. The dry ice snow comes out of the machine at -110°F. This treatment is non-toxic, contains no chemicals, and is effective for the bed bugs that it reaches. It is safe for most surfaces including electronics. This makes it useful for treating bed bugs inside cars, trucks, trailers, and other vehicles where high heat or chemicals would not be recommended. However, as with all bed bug treatments with no chemicals, it provides no residual. Cryonite is not intended to be used as a stand-alone treatment. It should be used in conjunction with other bed bug elimination procedures such as mattress and box spring encasements, active monitoring and trapping, vacuuming, and if circumstances allow, a chemical treatment for a residual effect.Video Player00:0000:28
What Is Cryonite?
Cryonite is the brand name of the newest bed bug treatment. It uses special equipment to turn liquid carbon dioxide (CO2, one of the same elements we breathe in and out) into dry ice particles, similar to snow.
A technician will then use a special nozzle to spray the dry ice on any surface where bed bugs may be. The dry ice has a temperature of approximately -110 degrees Fahrenheit, well below what bed bugs can withstand. It kills insects on contact and gets into the small crevices where bed bugs hide.
Benefits of Freeze Treatments for Bed Bugs
Insecticides have their place, and we still use them in many households or combine them with heat or freeze treatment. But temperature based treatments tend to be more reliably effective, especially for severe bedbug infestations.
Some of the many reasons that people appreciate temperature-based treatments is that they involve no chemicals, and leave no residue behind, making them safe to use around your children and pets. Since many bed bug infestations are often centered around high contact areas like beds and sofas, avoiding chemical treatments on these surfaces can give you extra peace of mind.
- Temperature treatments also have a greater success rate and reduce the chance that bed bugs will remain behind and enable the infestation to grow back.
- Both heat and cold treatments are effective. But, when compared with heat treatments, Cryonite offers many additional advantages:
- Less Costly – The equipment, power, and time needed to heat up an entire room are expensive and slow. Cryonite is targeted, so we can offer it at a fraction of the cost of heat treatments while providing the same results.
- Adaptable to Your Space – Cryonite works well in larger spaces where it would be impossible to raise the temperature enough to kill bed bugs. With freeze treatments, we can easily get to every area where bed bugs are hiding around a room.
- Safe for Belongings – As long as electronics are turned off, Cryonite will not cause any damage to them. It is also safe around furniture and other belongings. With heat, it is often necessary to take electronics out of the room first so the high temperatures do not melt delicate components. Bed bugs can hide in electronics as well, making cryonite more effective.
- Faster – Depending on the size of the room to be treated, heat treatments can take more than 6 hours. Cryonite works immediately.
- Cleaning Benefits – The freezing CO2 will also loosen dirt that may accumulate on surfaces. When you sweep up dead bed bugs after treatment, this dirt is easily swept up as well.
- No Need to Leave Your Home – Since freeze treatments are targeted to a small area, your family and pets can stay at home throughout treatment. You can also use any treated rooms almost immediately.
All of these benefits make bed bug freezing treatments better for residential properties, as well as many commercial properties. Only when a bed bug infestation is severe and in a small space that can be heated – like a hotel room – does a heat treatment make more sense.
In most infestations, the benefits of Cryonite make it the method of choice, but our bed bug specialists are experienced in all of the various bed bug control methods, including heat treatments and traditional pesticide-based treatments. After an inspection of your property, we can provide recommendations for which technique will be best.
We are also excited to explain more about the benefits of Cryonite bed bug treatments and the science behind this method. If bed bugs have been biting or have become an irritation on your property, call Nextgen Pest Solutions to take advantage of the industry’s most advanced treatment methods.
- Heat Treatment – Whole room heat treatments are a very effective natural bed bug treatment. A whole room bed bug heat treatment can be done by a Pest Management Professional in one day with specialized heaters. The room is monitored with temperature sensors and then heated up to between 135°F (57.2°C) and 145°F (62.7 °C). If necessary, fans are strategically placed in the room to aid with the distribution of the heat. If done correctly, the slowly rising temperature lures the bed bugs from the nooks and crannies where they hide and instantly kills both the bed bugs and their eggs when the temperature reaches 122°F (50°C). If the room or a particular hiding place does not reach the target temperature the heat treatment can fail. This natural method of killing bed bugs can take 6-8 hours for service. A whole room heat treatment offers no residual protection. A bed bug heat treatment is most successful when used with other bed bug elimination procedures such as mattress and box spring encasements, active monitoring and trapping, vacuuming, and if circumstances allow a chemical treatment for a residual effect. Without a chemical residual barrier, your room is not protected from a reintroduction of bed bugs.
How to Get Rid of Bed Bugs at Home
Many people choose to try and treat bed bugs themselves. While this can work for a time, often bed bugs will not be completely exterminated and will reappear and the infestation will grow.
After multiple unsuccessful DIY treatments, we find that people often spend as much money on treating bed bugs themselves as if they had called a pest management professional early on.
We recommend speaking to professional pest control companies and getting quotes for the service. Some companies even offer to finance a bed bug treatment. Successful bed bug treatments require a combination of multiple products, methods, and reapplication.
If you choose to get rid of bed bugs yourself, take your time, treat thoroughly, and retreat as often as necessary until there are no signs of bed bugs for at least 30 days.