Sleep tight and don’t let the bed bugs bite…
Remember that saying?
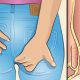
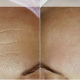
If you woke up recently with red rashes on your body or brownish markings on your blanket or pillowcases, chances are that you may have bed bugs. Today, bed bugs are a very serious problem.
These pests have spread significantly over the last two decades or more. They have become so common that almost everyone has experienced them at some point in their lives.
Bed bugs multiply quickly and are extremely difficult to eradicate. They may not pose a health risk to you. However, it’s inconvenient to have them crawling around in your bedding. So are the itches and skin sensitivities they create.
Do you travel often?
When you travel, these little bugs track into your house in your luggage, as well as in your handbags and your children’s school bags.
If you suspect that you have these unwelcome visitors in your room and you’re getting bed bug anxiety, here are 4 simple steps to take to get rid of them quickly:
Step 1: Early identification of bed bugs
Did you wake up one morning and suddenly have bites on your body that weren’t there when you went to sleep?
If you do, they could be bites from bed bugs.
Bed bug bites and stains on your bedding are some of the first signs of the presence of bed bugs. They cause welts on your skin and your skin itches.
Early identification of bed bugs is crucial for you to confine and eliminate the infestation. For starters, look for early symptoms of brown-black feces on your pillowcases, pillows, dashboards, bed springs, and mattresses, for example.
What do they look like?
It’s also important that you learn about these pests, how they spread, and the threats they pose to you. Incidentally, there are many other bugs, including carpet beetles, bat bugs, spider beetles, and roach nymphs, that have similar appearances.
So, you should now know what a bed bug looks like when you see one.
The adult pests, as well as their eggs, are visible to the naked eye despite their small size. They reproduce quickly and are able to go for months without feeding.

Bed bugs are external parasites that feed on human blood. They’re usually active at night, until a few hours before sunrise. They’re out at night, hunting for food, and then they hide throughout the day because they are sensitive to light.
The adult bed bug is brown and flat. You’ll find them in areas of your house or apartment that you frequent the most. This includes your bedroom and living room.
Once they have fed on a blood meal, their bodies become elongated and turn red.

Because bed bugs are rarely seen, you may wrongly believe you were bitten by mosquitoes, fleas, or spiders. Their bites can sometimes be mistaken for a common skin condition such as an itchy rash, hives, or chicken pox. To make sure you have bed bugs, you’ll need to do an inspection and look for signs of their presence.
Step 2: Inspection for bed bugs
Inspect the bites you have on your body. Bed bug bites are usually raised, they look like mosquito bites, and they are red in color.

Check your bedroom. An important step in eliminating these pests is to conduct a thorough inspection. Thoroughly inspect where you spend the most time, especially your bedroom.
For the inexperienced eye, looking for bed bugs is easier said than done. You must inspect many places where they can be found slowly and thoroughly.
Board
You may be able to see them if you have a huge infestation. The majority of people, on the other hand, only see signs of the presence of bed bugs.
Use a flashlight
Using a flashlight, look closely and thoroughly at your mattress. Look around the seams of the mattress. Look for signs of bed bugs, feces, dry blood, or skin shells.
Inspect behind your headboard, cracks in your bed frames, furniture, behind picture frames, and even the walls and electrical outlets.
Check your clock, TV, and radio. Inspect your dresser and chest of drawers, removing the drawers and inspecting them carefully. Bed bugs love to hide in cracks and crevices.
Here are positive signs you have bed bugs where you sleep:
A sweet, musty smell
Lie on your bed, close to your mattress, and take a deep breath. If you can smell a sweet, musty odor, you probably have an infestation. Not everyone is able to identify the characteristic smell generated by the chemicals produced by the bugs.
Specks of blood
Check for specks on:
- headboards
- bedding
- mattresses
- upholstered furniture.
Check your bedsheets, blankets, and mattress pads. Inspect your mattress and the box spring.
Did you notice specks of blood anywhere, particularly along the seams?
If you did, you likely have an infestation. Check for blood specks on upholstered furniture, such as couches and headboards.
Presence of tiny, blackish specks
It could be bed bug excrement if you detect blackish specks on your bedsheets, other bedding, mattress, headboard, or under your couch cushions.
Bed bug eggs
After mating, female bed bugs would lay white, round eggs in cracks and crevices. They’re usually the size of an apple seed, and their eggs are very tiny. You may see the eggs better by using a magnifying glass.
Bed bug exoskeletons
Bed bugs have an outer shell that they shed. If you look closely and find shell-like remains on your mattress, mattress pad, or beneath your couch cushions, those were left by the bugs.

After you’ve inspected your bedroom, inspect the rest of your house or apartment. This includes the areas you frequent a lot.
This includes the kitchen, living room, dining room, and other bedrooms.
Step 3: Treatment and control of bed bugs
Treating your bites
At-home treatment
If you don’t have signs of an infection or a serious reaction to the bites, you can treat them at home.
- Wash the bites with soap and water to reduce itchiness and prevent skin infection.
- Apply a corticosteroid lotion to the bites if they itch. Cortizone 10 is the maximum strength of corticosteroids that you can buy over the counter. It provides relief for the itchiness.
Corticosteroids of a higher potency will require a prescription from your doctor. In most cases, your bites will heal and disappear within a week or two.
When to see your doctor
You should see a doctor or dermatologist if you have:
- Many bites
- Blisters resulting from the bites
- An allergic reaction like red and swollen skin or hives
- Skin infection from the bites. If your bites feel tender or there’s a discharge or pus, you need to see a doctor immediately. Those are signs of an infection.
Treating your home
Prepping the room
Remove bedding and clothing material. Wash them in hot water and heat-dry them. Place them in a plastic bag and store them away from the room that you’re about to treat.
Disassemble the furniture in the room to be treated. This will help you have access to the cracks and crevices.
Thoroughly vacuum the room.
Using the proper attachments for your vacuum cleaner, vacuum your mattress, especially at the edges. Vacuum your box springs and around your baseboards.
If you’re using a bag vacuum cleaner, dispose of it outdoors. If your vacuum cleaner is a canister type, empty it outdoors and thoroughly rinse it out to remove any eggs or immature stages of the bug that you may have picked up.
Chemical control
Step 1: Don safety work gloves. Using a spray tank, spray Bed Bug Killer onto your mattress, including around the seams. If there are any buttons on the surface of your mattress, spray around those as well.
Step 2: Add Gentrol Concentrate directly to the Bed Bug Killer in your spray tank. Gentrol is an insect growth regulator that will prevent pests from reproducing.
Remove the net from the bottom of your box spring and spray this mixture into the cracks and crevices. Spray the entire floor area in the room, including the floors that are adjacent to the room. This keeps the bed bugs in the room you’re treating from moving to other rooms.
Step 3: Next, spray the cracks and crevices of all the furniture in the room:
- The bed frame.
- Bedside table.
- Dresser.
- Chest of drawers.
Step 4: Apply Bed Bug Killer Dust to cracks inside the walls.
This will prevent the pests from moving from one room to another. Inject this powder underneath the baseboards.
Turn off the breaker to the electrical outlets in the room and remove the covers from all electrical outlets. Inject the treatment dust in there as well. Apply the dust to large voids in the cracks of the furniture in the room.
Repeat steps 1 – 4 every couple of weeks until you no longer have bed bug activity.
Then repeat the treatment at least every six months as needed.
If you travel a lot, you should repeat this process every time you return from a trip. This will prevent you from reintroducing bed bugs into your home.
Step 5: Protect your mattress and box springs using hypoallergenic, breathable mattress and box spring encasements.
Step 4: Prevention of reinfestation
If you live in an apartment, you may need to move away to avoid reinfestation from adjoining apartments.
Do you travel a lot?
If you travel frequently and stay in hotels, you should take precautions when you return home. Wash all clothing in hot water and vacuum all the seams and pockets inside your suitcases and purses.
If you follow this four-step process, you’ll be guaranteed to eliminate the bugs from your home.